ContentModels in HTML 4 were previously defined in two models: Inline and Block. HTML 5 now offers seven different models, each of them representing a broad category.
According to the new specification, each defined element has a content model which is a description of the element's expected contents. An HTML element must have contents that match the requirements described in the element's content model.
The specification goes on to say: “Authors must not use HTML elements anywhere except where they are explicitly allowed, as defined for each element, or as explicitly required by other specifications.” “Each element in HTML falls into zero or more categories that group elements with similar characteristics together.”
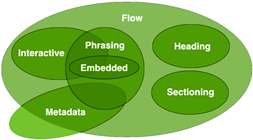
- The following broad categories are used in this specification:
- Metadata: Sets up presentation or behavior
- Embedded: Imports other resources
- Interactive: User interaction intentionality
- Phrasing: Text and elements of the document
- Flow: Normally included elements
- Sectioning: Defines scope
- Heading: Defines section headers
Some elements also fall into other categories, which are defined in other parts of the specification. Which means some categories overlap. Read more about Content Models.